Borrelia
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato
Infection route
Transmission occurs via the bite of infected ticks. The Borrelia bacteria are transmitted to humans after a few hours during the biting and sucking act of the tick. Not all ticks are infected and not every tick bite leads to Lyme disease. The risk of infection is about 5%. There is no transmission from human to human.
Symptomatology
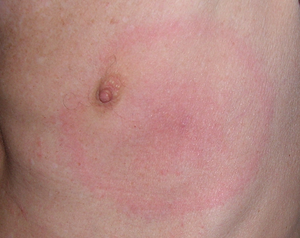
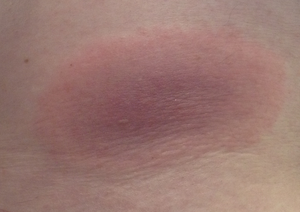
A typical ring-shaped, reddish rash called erythema migrans or wandering redness occurs in about 85% of cases. Headache, fever, fatigue or joint pain may also occur. With proper and prompt treatment, symptoms resolve quickly.
Another form of Lyme disease affects the nervous system: a few weeks after infection, meningitis and facial nerve paralysis may occur, especially in children, and painful nerve root inflammation and paralysis in adults. Other rare forms include joint inflammation and typical skin lesions on the extensor sides of the extremities. In most forms, timely antibiotic treatment leads to sustained improvement; untreated, Lyme disease can lead to long-lasting symptoms.
Situation in Austria
Lyme borreliosis is a frequently diagnosed disease in Austria, but is not notifiable. It is estimated that 25,000 to 70,000 people contract the disease every year. Most cases are observed in spring and summer, when people spend more time outdoors and are bitten more frequently by ticks.
As part of a research project, a national tick surveillance programme has been running since the beginning of 2024, in which ticks are also tested for Borrelia, among other things.
Specialized information
Lyme disease, borreliosis or Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by bacteria from the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex. This term includes those Borrelia species that cause most infections in Europe: B. afzelii, B. garinii, B. bavariensis, and B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. The common wood tick(Ixodes ricinus) is the most common vector of Borrelia in Europe.
The development of Ixodes ricinus includes three stages: larva, nymph, and adult (adult) tick. Small rodents or birds are the most common hosts for larvae, and larger rodents or medium-sized mammals, such as cats or dogs, for nymphs. Larger hosts, such as deer and deer, are important blood hosts for adult ticks, but are not reservoirs of Borrelia. Ticks pick up borrelia from one host animal during a blood meal and pass it on to the next host.
Erythema migrans (wandering redness) is the most common disease symptom of Lyme borreliosis (> 80 percent of all cases). Erythema migrans develops at the earliest 3-6 days up to several weeks after the tick bite around the tick bite site as an enlarging red or blue-red spot with or without later central lightening. The outer edge is clearly separated, often more intensely colored and not noticeably raised. If the diameter is at least five centimeters, the diagnosis is made clinically by an experienced physician. If the diameter is smaller, the diagnosis requires a confirmed tick bite, a delay of at least two days in the appearance of the erythema after the tick bite, and increasing erythema at the tick bite site.
Accompanying symptoms such as local itching/burning, fatigue, headache, joint pain can occur with erythema migrans with a frequency of 40%.
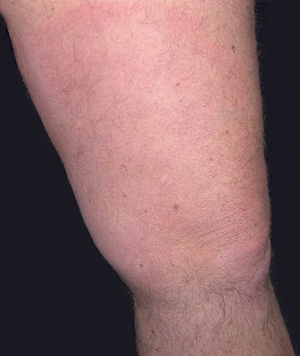
Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA) is a chronic progressive skin disease caused by Lyme borrelia that does not heal spontaneously. ACA begins with a red or blue-red change in the skin, usually on the extensor sides of the arms or legs, which may persist for a long time. Later, there is a disappearance of all skin layers (skin atrophy), the skin becomes thin "like cigarette paper" and easily vulnerable. Neuropathies (damage to nerves) may occur in the affected skin area. With long-standing ACA, the joints in the affected skin area are also affected. Skin thickening and slowly growing, painless, fibroid nodules (benign tumors) may develop over bony prominences.
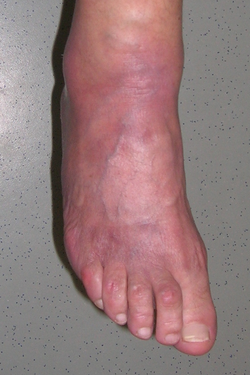
Lyme neuroborreliosis occurs in adults mainly as meningitis and as very painful nerve root inflammation (Garin-Bujadoux-Bannwarth syndrome). Rarely, brain inflammation (encephalitis), spinal cord inflammation (myelitis), and very rarely inflammation of the brain vessels (cerebral vasculitis) are observed.
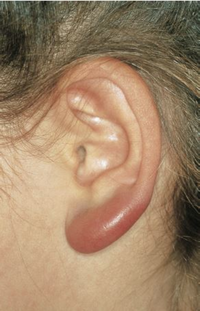
In children, Lyme neuroborreliosis mainly manifests as facial paralysis or mild meningitis.
Therapy
Lyme disease is treated with antibiotics. Various treatment options are available for this. The duration of treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
Early forms of Lyme disease are usually treated with oral or intravenous antibiotics over a period of 10 to 14 days.
Late forms are treated over four weeks. Most patients respond well to antibiotic therapy and show improvement in their symptoms. This is especially true for erythema migrans and neuroborreliosis. Timely treatment of Lyme borreliosis is important to avoid possible late sequelae.
Diagnostic
The diagnosis of erythema migrans can be made by the physician purely clinically - i.e. that no laboratory examination is necessary. All other forms require blood testing for antibodies.
Serologic tests can be used to detect antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi. In early stages of the disease, these tests may be falsely negative. In late forms, antibodies are always present.
Interpretation of results is sometimes difficult because even healthy individuals may have antibodies to Borrelia. That is why the correlation with symptoms is important in the evaluation. To confirm the suspicion of Lyme neuroborreliosis, the serum and cerebrospinal fluid must be taken and examined with special methods. Direct pathogen detection of Borrelia (PCR, culture) is not suitable for routine diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis.
Contact
Priv.-Doz. Dr. med Mateusz Markowicz
- mateusz.markowicz@ages.at
- +43 50 555 37204
- Währingerstraße 25a, 1090 Wien
Last updated: 07.10.2024
automatically translated